Define Neuron and Describe the Structural Components
At one end of the cell body and indeed around most of its periphery are many small branching protrusions called dendrites. But the truth is that there are other structures that allow these neurons to be the pillar of the nervous system and therefore of everything that happens in.
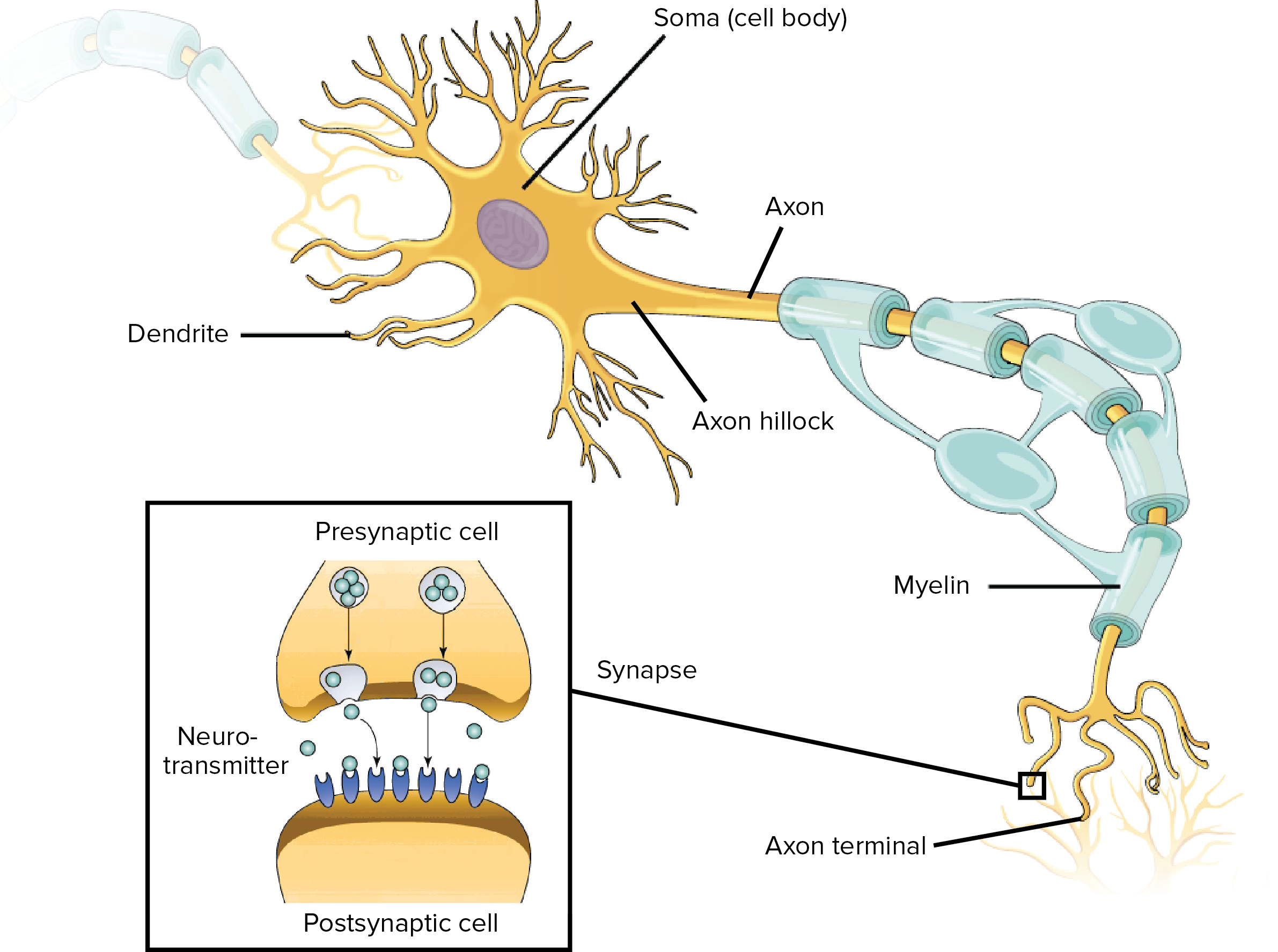
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system.

. A cell body an axon and dendrites. A dendrite tree branch is where a neuron receives input from other cells. PerikaryonSoma - body the center of biosynthesis.
Dendrites and axons both extend from. Specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body Dendrites. Treelike extensions from the beginning of a neuron that receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the Soma Cell body Soma Cell Body.
They are basically divided into three regions. The signals received are in the form of electrical signals. These parts help them to send and receive chemical and electrical signals.
Neurons are responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body a process that allows us to move and exist in the world around us. Nerve cells or neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system. These specialized cells are the information-processing units of the brain responsible for receiving and transmitting information.
5 rows Neuron Structure. Lower motor neurons these are neurons which travel from the spinal cord to the muscles of the body. Neurons are the primary components of the nervous system along with the glial cells that give them structural and metabolic support.
Almost all neurons however have three basic components. Learn about our editorial process. Neurons have highly branched fibres that reach out from the neuron are called dendritic trees.
The structure of neuron. Dendrites receives messages from the surrounding and sends it to the cell body. The structure of a neuron varies with their shape and size and it mainly depends upon their functions and their location.
The cell body of the neuron contains the nucleus. There are two types of motor neurons. Differentiate between a nerve and a tract and between a nucleus and a ganglion.
Biosynthetic center of neuron Synthesizes proteins membranes and other chemicals Rough ER chromatophilic substance or nissl bodies Most active and best developed in body Spherical nucleus with nucleolus In most plasma membrane part of receptive region Most neuron cell bodies in CNS Nuclei - clusters of neuron cell bodies in CNS. They are found in the brain spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Upper motor neurons these are neurons which travel between the brain and the spinal cord.
It contains the nucleus and other structures common to all cells in the body such as mitochondria. Neurons do not touch each other but where one neuron comes close to. Where signals from dendrites are joined and passed on.
Treelike extensions from the beginning of a neuron that receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the Soma Cell body Soma Cell Body. Body dendrites and soma. It consists of three major parts namely cell body dendrites axon.
The structure of a motor neuron can be categorized into three components. Each neuron has a cell body with a nucleus Golgi body endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria and other components. Where signals from dendrites are joined and passed on.
Neurons also known as nerve cells are essentially the cells that make up the brain and the nervous system. Cell body consists of nucleus mitochondria and other organelles. Each neuron has a cell body which is the central area of the neuron.
The cell body is in charge of carrying genetic information keeping the neurons shape and giving it the energy it needs to move. The size shape and structure of neurons vary based on their function and location. Nerve processes exist as either dendrites or axons.
Each part of the neuron plays a role in communicating information throughout the body. Extending from the other end of the cell body at a location called the axon hillock is the axon a long thin tube-like protrusion. It is irregular in shape or polyhedral.
Neurons are the information processing units of the brain which have a responsibility for sending receiving and transmitting electrochemical signals throughout the body. Structure of Neuron. The soma the axon and the dendrites.
The nucleus of the neurons cell body contains its DNA or genetic material. A neuron is a specialized cell primarily involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. Axon transmits the message away from the cell body and pass it to the next receiving neuron.
Structure of a neuron. Neurons are cells with a very characteristic morphology. The main three parts of a neuron are the cell body or soma axon and.
A neuron has three main parts. The nervous system is made up of the central nervous system which includes the brain and spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system which includes the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. Tract- CNS collection of axons.
A neuron is also known as the nerve cell. The structure of a neuron can be described as a cell body with nerve processes that transmit signals from one neuron to another. It is the chemical junction between the terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another neuron.
Dendrites an axon and a cell body or soma see image below which can be represented as the branches roots and trunk of a tree respectively. They have three distinct parts including a cell body axon and dendrites. Each branch is called a dendrite.
Nervous system cells are called neurons. Axon is a tube-like structure that carries electrical impulse from the cell body to the axon terminals that passes the impulse to another neuron. Neuron comprises dendrite axon and cell body.
Different types of neurons include sensory motor and interneurons as well as structurally-based neurons which include unipolar multipolar bipolar and pseudo-unipolar neurons. Define neuron describe its important structural components and relate each to a functional role. Specialized cells that conduct messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body Dendrites.
4 1 The Neuron Is The Building Block Of The Nervous System Introduction To Psychology 1st Canadian Edition
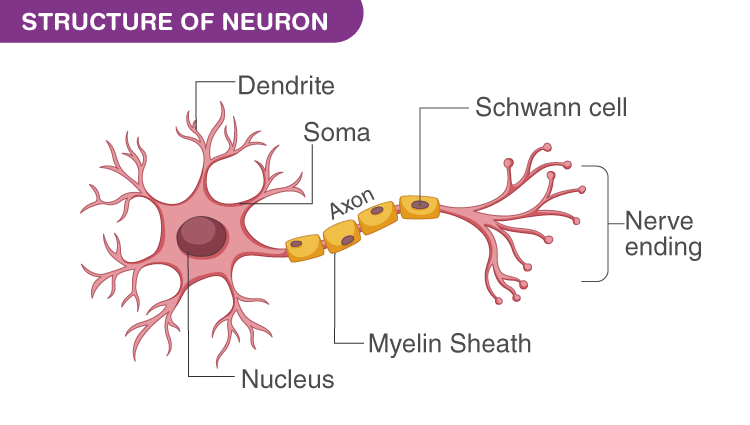
What Is A Neuron Definition Structure Parts And Function
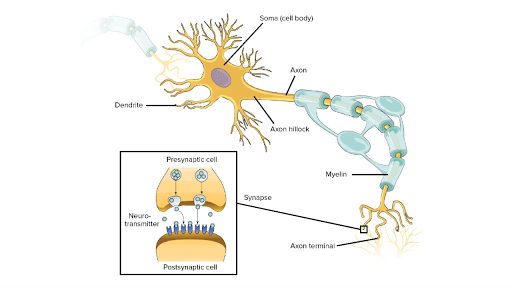
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
Comments
Post a Comment